Definitions:
- Multimeter- a device used to measure voltage, current, or resistance.
- Voltage- a measurement of the electric field potential to create a current in a conductor.
- Current- a measurement of how much charge moves through a circuit during a specific period of time.
- Resistance- how freely electrons can flow through materials because of a voltage (move less freely= more resistance and less conductivity)
- Ohm’s law- relates voltage to current and resistance. V= I*R
I. Basic Electronic Components:
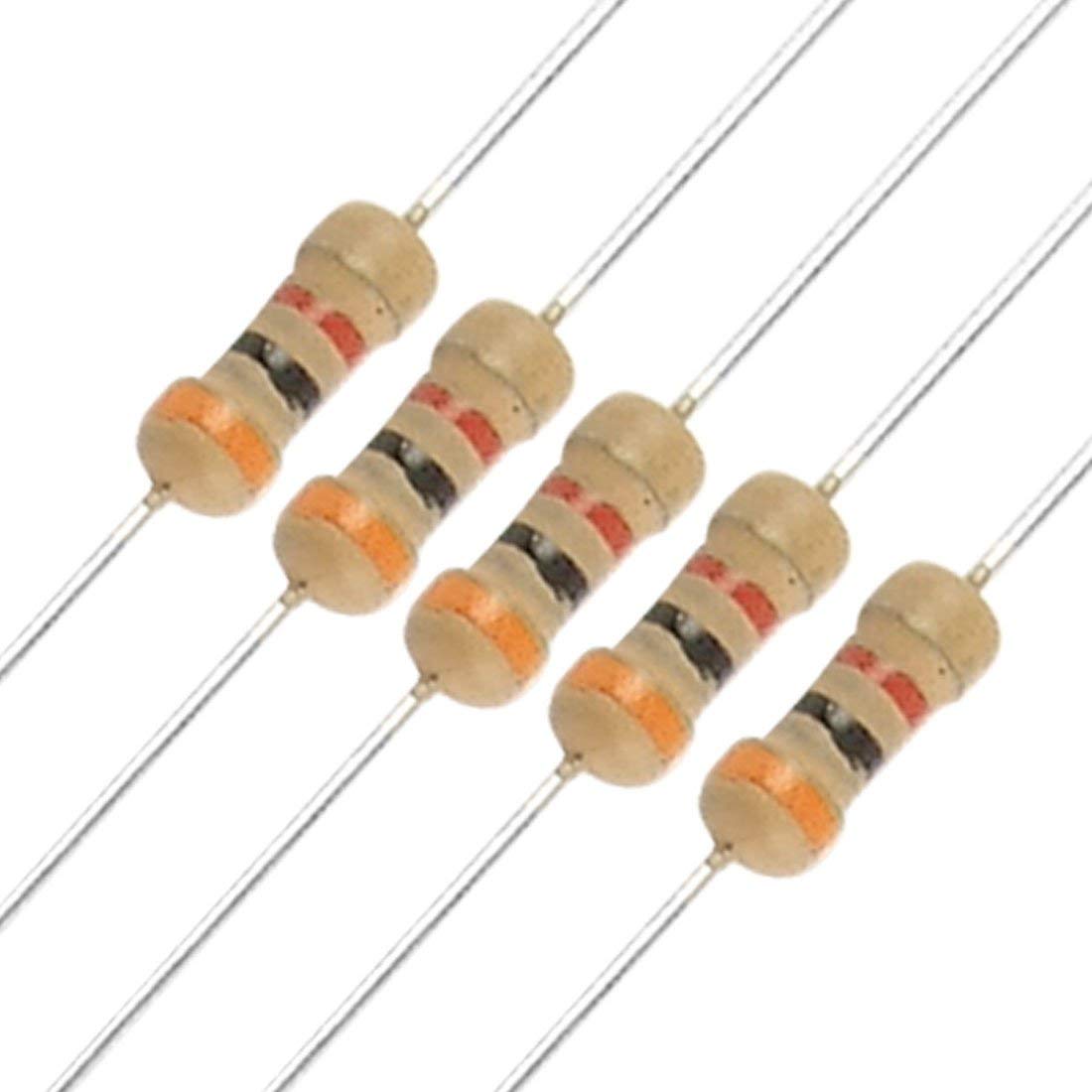
a. Resistors:
- Restrict the flow of electric current.
- Can be connected to circuit either way.
- Are not damaged by soldering.
- Resistor colour code:
1st band= 1st digit
2nd band= 2nd digit
3rd band= # of zeros
4th band (can be ignored)= tolerance
There are also special bands: Gold= x0.1, Silver= x0.01
b. Variable Resistors (AKA Potentiometers):
- Have a resistance track and wiper that moves along as you turn a spindle.
- Linear tracks- the resistance will change at a constant rate.
- Logarithmic tracks- the resistance will change slowly at 1 end and rapidly at the other.
c. Capacitors:
- Store electric charge.
- Polarized Capacitors (AKA Electrolytic capacitors)- must be connected a certain way in the circuit. Note: the long lead is positive. Polarized caps aren’t damaged by heat from soldering.
- Unpolarized Capacitors can be connected either way and also will not suffer heat damage from soldering.
- Capacitors have the same colour/number code as resistors.
d. Diodes:
- Allow electricity to flow in only 1 direction (like a valve).
- Have polarity and thus must be connected a certain way. Note: the side with the line on it is negative.
- Signal Diodes- used for small currents. Process information in circuits, and protect transistors and ICs (integrated circuits) from high voltage.
- Rectifier Diodes- used for large currents. Convert AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current) in a power supply.
- Zener Diodes- used to maintain a fixed voltage. Will allow electricity to flow both ways.
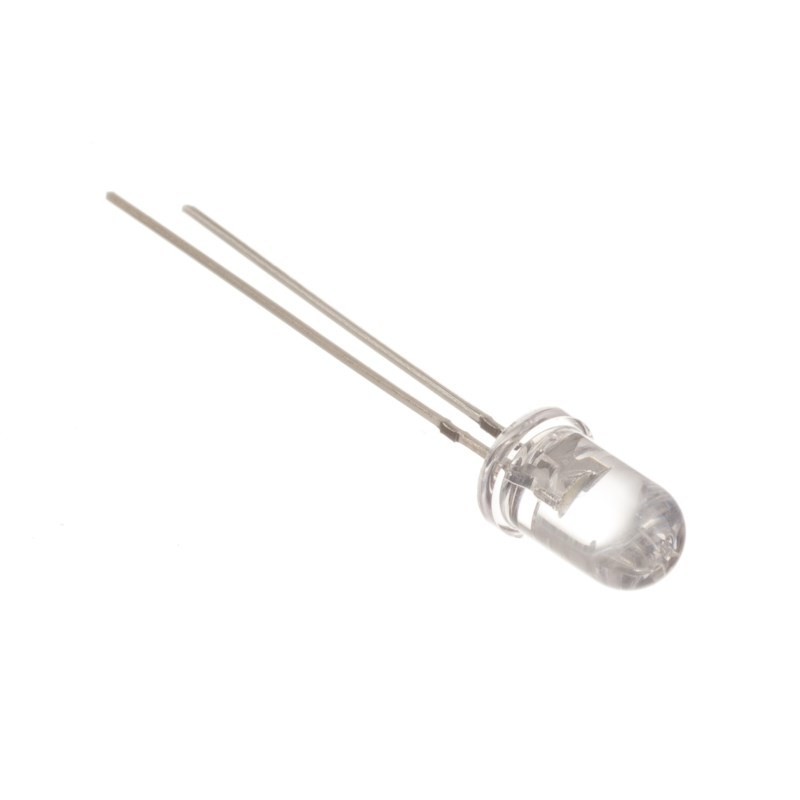
e. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs):
- A different type of diode.
- Will emit light when an electric current passes through them.
- Should not be hooked up directly to a power source.
- Have polarity and thus must be connected a certain way. Note: the small lead is negative.
f. Transistors:
- Have polarity and thus must be connected a certain way or they will be immediately damaged.
- Can be damaged by soldering heat, so you should use a heat sink when soldering.
- Amplify current, voltage, or can be used as a switch.
g. Integrated Circuits (ICs):
- Complex circuits that are etched into tiny semi-conductor chips.
- Can be damaged easily by soldering heat, so you should use an IC holder when soldering and then pop the IC in.
- Many are static sensitive.